The 10-Second Trick For Dementia Fall Risk
The 10-Second Trick For Dementia Fall Risk
Blog Article
Some Of Dementia Fall Risk
Table of ContentsMore About Dementia Fall RiskNot known Details About Dementia Fall Risk The 7-Second Trick For Dementia Fall RiskDementia Fall Risk Things To Know Before You BuyGetting The Dementia Fall Risk To Work
The FRAT has three areas: drop threat condition, threat factor list, and action plan. A Loss Risk Status consists of information regarding history of current falls, medicines, psychological and cognitive status of the person - Dementia Fall Risk.If the individual ratings on a threat aspect, the equivalent number of factors are counted to the individual's autumn danger rating in the box to the far. If an individual's loss threat score amounts to 5 or greater, the individual is at high danger for falls. If the client scores just 4 factors or lower, they are still at some danger of dropping, and the registered nurse needs to use their finest clinical assessment to manage all autumn danger elements as part of a holistic care strategy.
These common techniques, in basic, help develop a safe environment that decreases unexpected falls and marks core safety nets for all clients. Indications are essential for individuals in jeopardy for drops. Doctor need to recognize who has the condition, for they are in charge of implementing actions to promote individual safety and security and protect against falls.
What Does Dementia Fall Risk Mean?
As an example, wristbands must include the client's last and given name, date of birth, and NHS number in the UK. Details must be printed/written in black against a white history. Only red shade needs to be utilized to signal special patient condition. These recommendations are consistent with present advancements in client recognition (Sevdalis et al., 2009).
Items that are also far may call for the individual to connect or ambulate needlessly and can potentially be a danger or add to falls. Helps protect against the patient from heading out of bed without any aid. Nurses reply to fallers' telephone call lights faster than they do to lights launched by non-fallers.
Aesthetic problems can considerably trigger drops. Maintaining the beds closer to the floor decreases the danger of falls and severe injury. Placing the bed mattress on the flooring substantially minimizes fall risk in some healthcare settings.
The Greatest Guide To Dementia Fall Risk
Clients who are tall and with weak leg muscle mass who attempt to rest on the bed from a standing position are most likely to fall onto the bed since it's too reduced for them to lower themselves safely. Additionally, if a tall client efforts to stand up from a low bed without support, the patient is likely to fall back down onto the bed or miss out on the bed and drop onto the floor.
They're designed to advertise timely rescue, not to prevent drops from bed. Aside from bed alarms, enhanced guidance for high-risk clients additionally may aid stop drops.
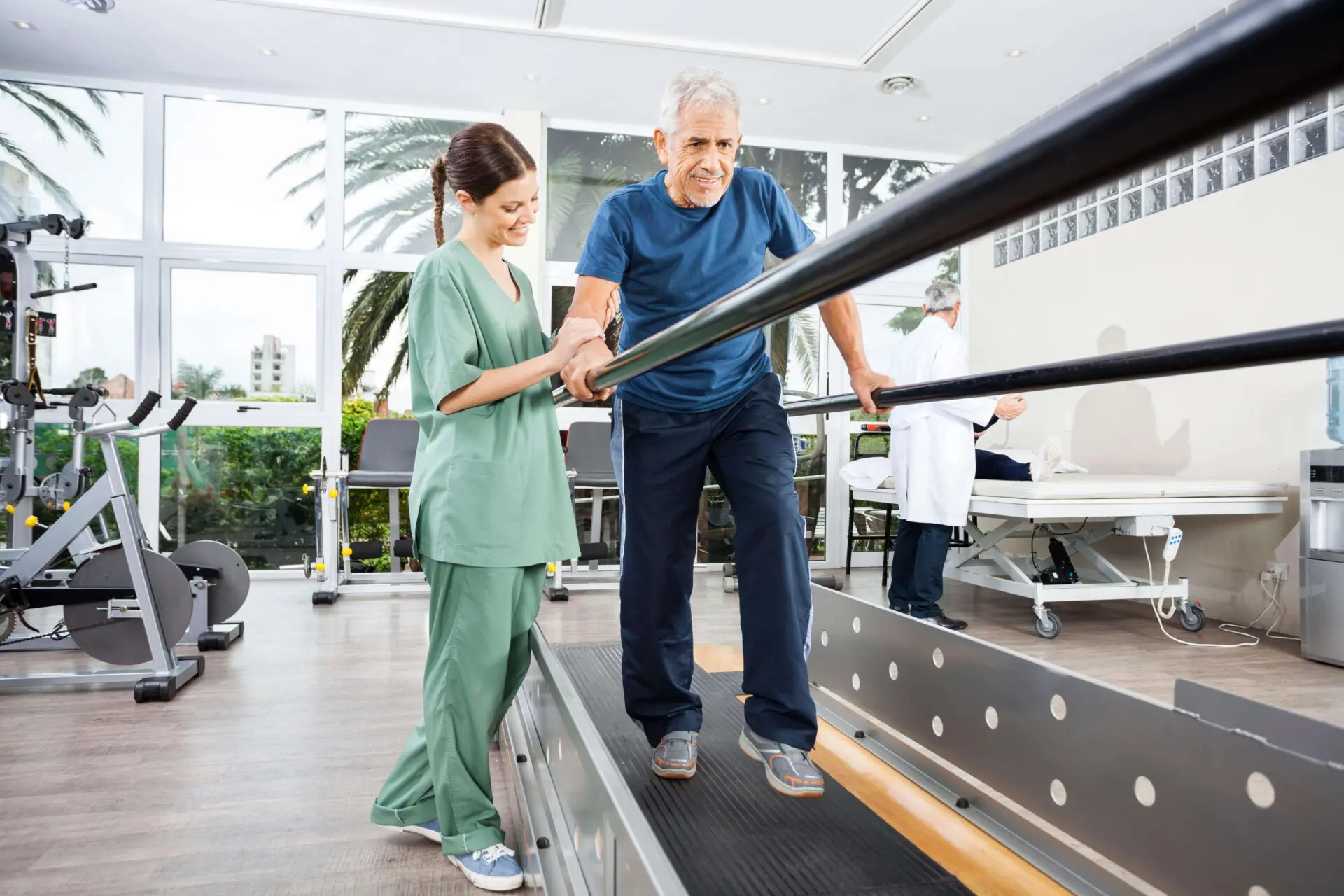

Clients with an evasion stride rise autumn opportunities considerably. To lower fall danger, shoes should be with a little to no heel, thin soles with slip-resistant walk, and sustain the ankle joints.
A Biased View of Dementia Fall Risk
In a study, homes with sufficient lighting report fewer falls (Ramulu et al., 2021). Enhancement in illumination at home might lower autumn prices in older adults.

Caretakers work for ensuring a safe and secure, protected, and safe environment. Research studies showed extremely low-certainty proof that caretakers minimize autumn threat in severe care medical facilities and just moderate-certainty that options like video tracking can decrease caretaker usage without boosting fall risk, recommending that sitters are not as useful as at first believed (Greely et al., 2020).
A Biased View of Dementia Fall Risk
Enhanced physical fitness lowers the risk for drops and limits injury that is received when loss transpires. Land and water-based workout programs might be likewise helpful on balance and stride and thus reduce the risk for falls. Water exercise may contribute a positive benefit on equilibrium and gait for females 65 years and older.
Chair Increase Exercise is a simple sit-to-stand exercise that assists reinforce the muscular tissues in the upper legs and butts and improves wheelchair and independence. The objective is to do Chair Increase workouts without utilizing hands as the customer becomes more powerful. See resources section for a thorough direction on exactly how to perform Chair Increase exercise.
Report this page